Located in London, I measured the RTT or round trip time to 574,691 random webservers and plotted the times on the globe.

Discovery was done with masscan, measurements using hping and plotting with an old Python script I’ve revived and enhanced.
This is part of the next writeup on my blog, with which I will be posting any of the code I’ve used.

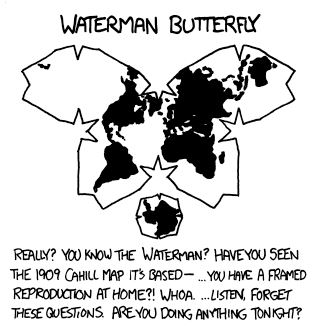
Thank you very much for that in-depth explanation!
If you have any more of that, I’d be very interested :-)
This is just what i picked up from my colleagues at work while i was helping them with electronics trouble in their lab. They are doing research using attosecond length laser pulses, which is why they needed to use hollow core stuff to keep the signal fast and clean. If you dont remember what atto means those pulses are 0.000000000000000001 seconds long (well in that range not actually 1 attosec more like tens to hundreds of attosecs). But yeah thats all i know ^^
For more technical details from Wikipedia: